
 |
Freethought & Rationalism ArchiveThe archives are read only. |
|
|||||||
|
|
Thread Tools | Search this Thread |
|
|
#1 |
|
Contributor
Join Date: Mar 2006
Location: Falls Creek, Oz.
Posts: 11,192
|
The Christian historians got it wrong purposefully. Arius the master heretic, described as the "Antichrist" by the orthodox, was not a "christian presbyter". The alteration from Platonist to Christian was a way of explaining the victorious ascent of the Christian religion to later generations of the faithful. I have written an essay on this subject entitled A Pageant of Christian Identity Frauds masquerade in the Academy of Plato
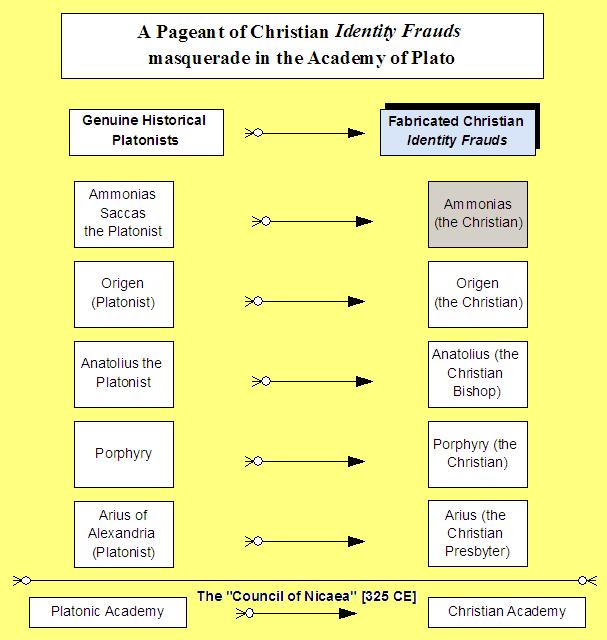 Does anyone have any ideas about how I might get this essay peer reviewed? FYI I have conducted many years of research but outside of any academic institution. This recent essay is a product of my research. How might I get critical comments on this idea from the academic institutions? Best wishes, Pete |
|
|
|
|
#2 | |
|
Contributor
Join Date: Mar 2006
Location: Falls Creek, Oz.
Posts: 11,192
|
This has been reposted from another thread I was reading Plutarch.
Quote:
FWIW here are my notes .... The Legacy of Greece - Oxford University Press (1921) RELIGION by W. R. Inge, Dean of St.Paulsp.26 "Greece for our purposes means not a race, but a culture, a language and literature, and still more an attitude towards life, which for us begins with Homer, and persists, with many changes but no breaks, till the closure of the Athenian lecture rooms by Justinian. The civilization of the Roman Empire was not Italian but Greek. It was lost to the West for nearly a thousand years. It was recovered at the Renaissance, and from that time to this has been a potent element in Western civilization. The Dark Ages and the early Middle Ages are the period in which the West was cut off from Hellenism ... These were the ages of the Catholic theocracy; and if we choose one man as the founder of Catholicism as a theocratic system, we should have to name neither Augustine not St.Paul,still less Jesus Christ, but Plato, who in the Laws sketches out with such wonderful prescience the conditions for such a polity, and the form which it would be compelled to take." Hellenism then is not the mind of a particular ethnic type, not of a particular period. It was not destroyed, though it was emasculated, by the loss of political freedom; it was neither killed nor died a natural death. Its religion passed into Christian theology without any real break. The early church spoke in Greek and thought in Greek. p.29 It is quite unnecessary to look for Asiatic influences in a school which clung close to the Attic tradition. It should not be necessary to remind Hellenists that "Know Thyself" passed for the supreme word of wisdom in the classical period, or that Heraclitus revealed his method in the words "I searched myself". "The teachings of Plato", says Justin, "are not alien to those of Christ; and the same is true of the Stoics." "Heraclitus and Socrates lived in' accordance to the divine Logos" and should be recognised as Christians. Clement says that Plato wrote "by the inspiration of God". Augustine, much later, finds that "only a few words and phrases" need to be changed to bring Platonism into complete accord with Christianity. The ethics of contemporary paganism, as Harnack shows,with special reference to Porphyry,are almost identical with those of the Christians of his day. Catholic Christianity is historically continuous with the old civilization, which indeed continued to live in this region after its other traditions and customs had been shattered. There are few other examples in history of so great a difference between appearance and reality. Outwardly, the continuity with Judaism seems to be unbroken, that with paganism to be broken. In reality, the opposite is the case. p.33 Further,too much is made of the conflict between the official cults of paganism and Christian public worship. It is forgotten how completely, in Hellenistic times, religion and philosophy were fused. Without under- estimating the simple piety which, especially in country districts, still attached itself to the temples and their ritual, we may say confidently that the vital religion of the empire was associated with mystery-religions and with the discipline of the "philosophic life". p.42 Their sacrifices were for the most part of the genial type, a communion meal with the god. But even in Greece, we must remember the gloomy chthonian rites, and the degradations of Orphism mentioned by Plato in the "Republic".
This exploitation of sacramentalism was common enough in Greece; but the characteristic Caesaro-Papism of Byzantium and modern imperium was wholly foreign to Hellenism. It was introduced by Constantine as part of the Orientalizing of the empire begun by Diocletian. As Seely says:
The Greeks never had a book religion, in the sense that Judaism became, and Islam always was, a book religion. But they were in some degree of treating Homer and Hesiod as inspired scriptures. To us it is plain that a long religious history lies behind Homer, and that the treatment of the gods in Epic poetry proves that they had almost ceased to be the objects of religious feeling. Some of them are even comic characters, like the devil in Scottish folklore. To turn these poems into sacred literature was to court the ridicule of the Christians. But Homer was never supposed to contain "the faith once delivered to the saints"; no religion of authority could be built upon him, and Greek speculation remained far more unfettered that the thought of Christendom has been until our own day. p.45 Nothing can be further from the truth than to call the Greeks "intellectualists" in the disparaging sense in which the word is now often used. The object of philosophy was to teach a man to live well, and with that object to think rightly about God, the world and himself. This close union between metaphysics, morals and religion has remained as a permanent possession of the modern world. The Hellenistic combination of Patonic metaphysics with Stoic ethics is still the dominant type of Christain religious philosophy. Asceticism has a continuous history within Hellenism. Even Homer knows of the priests of chilly Dodona, the Selli, whose bare feet are unwashed, and who sleeps on the ground. The worship of Dionysus Zagreus in Thrace was accompanied by ascetic practices before Pythagoras. Vergetarianism, which has always played an important part in the ascetic life, was obligatory on all Pythagoreans. http://www.mountainman.com.au/essene..._of_Greece.htm |
|
|
|
|
|
#3 |
|
Contributor
Join Date: Jun 2000
Location: Los Angeles area
Posts: 40,549
|
I think you got one of your previous papers peer reviewed. It did not go well.
If you are really serious about any sort of peer review, find a university course, even an online university, and take a course from a real professor. Submit your paper or part of it as a course assignment, get feedback, and take the criticisms seriously. Revise your paper in light of the criticisms. That's how things work. |
|
|
|
|
#4 |
|
Contributor
Join Date: Mar 2006
Location: Falls Creek, Oz.
Posts: 11,192
|
Thanks Toto. It is true that the Referee Report from JHL (2007) was unfavorable, and I think the reviewer searched BC&H at that date, and incorporated such responses as:
This is a revival of the theses of Athanasius Kircher and the AbbÈ Hardouin, who (in the hope of disarming the protestant appeal to primitive Christianity) argued that the whole corpus of ancient literature, including the Fathers, up to about 900 A.D. is a forgery. The reasoning of Kircher was based on the absence of numismatic corroboration for the written testimonies. There is a critical problem with such a comparison and that is the C14 evidence (3rd/4th century CE), which my thesis uses to support its claims, and which immediately destroys the theory of Athanasius Kircher and the AbbÈ Hardouin. The reasoning of my theory certainly analyses the numismatic evidence, but is certainly not based upon it. In any event, it was a good exercise at the time, and one that demonstrated that I am considering these matters more seriously than most. It was almost 4 years ago. How time flies when you're having fun. Yesterday we were not here, today we are here, tomorrow we are gone. Peace. |
|
|
| Thread Tools | Search this Thread |
|